Discover Health Benefits of Magnesium Chelated Blends Today
Table of Contents

You can experience real health benefits by choosing a magnesium chelated blend. Magnesium chelate forms, such as chelated magnesium and magnesium chelate, use a chelation process that helps your body absorb this mineral better. Many clinical studies show chelated magnesium supports heart health, muscle relaxation, mood, sleep, and even brain well-being. People often report less muscle soreness, better blood sugar control, and fewer headaches with magnesium chelate.
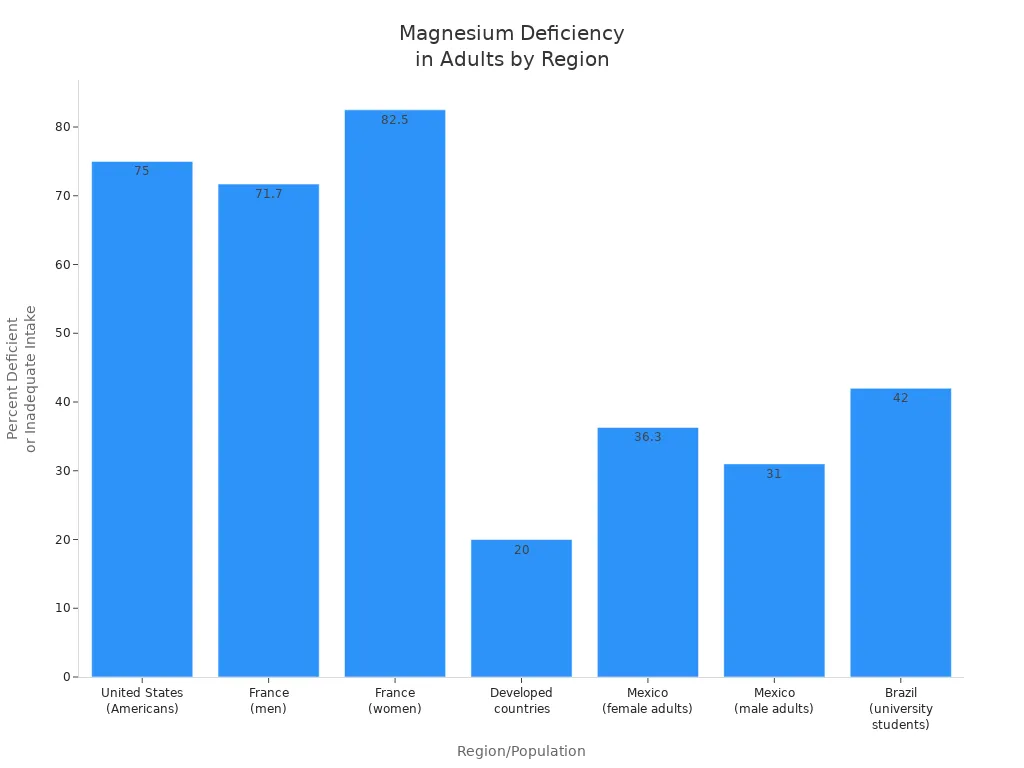
Did you know that about 75% of adults in the United States do not get enough magnesium?
| Region/Population | Percentage Magnesium Deficient or Inadequate Intake |
|---|---|
| United States (Americans) | ~75% magnesium deficient |
| France (men) | ~71.7% inadequate intake |
| France (women) | ~82.5% inadequate intake |
| Developed countries (general) | 10-30% subclinical magnesium deficiency |
| Mexico (female adults) | 36.3% low serum magnesium |
| Mexico (male adults) | 31% low serum magnesium |
| Brazil (healthy university students) | 42% subnormal magnesium status |
Magnesium chelated blends matter for your wellness and daily health because they make it easier for your body to get the full benefits of this vital mineral. You can trust magnesium chelate to support your well-being with proven effectiveness and gentle digestion.
What Is Chelated Magnesium?
Definition
You may wonder what chelated magnesium means. Chelated magnesium is a special form of magnesium where the mineral bonds to an organic molecule, often an amino acid. Experts describe chelated magnesium as a compound with magnesium attached to a chelate, such as glycine or aspartic acid. This bond creates a stable structure that your body can absorb more easily. For example, magnesium glycinate is a chelated magnesium where magnesium connects to glycine. This form is gentle on your stomach and recommended for daily use. Magnesium chelate mimics the way your body naturally handles minerals, making it easier for you to get the benefits.
Tip: Magnesium chelate blends, like magnesium glycinate, are less likely to cause digestive upset than other forms.
How It Works
The chelation process starts when magnesium ions form strong bonds with ligands, such as amino acids. This process creates chelated magnesium, which stays stable in your digestive system. Unlike non-chelated magnesium salts, such as magnesium oxide, chelated magnesium does not break apart quickly. The chelate structure helps magnesium pass through your intestinal wall using special transport pathways. This leads to improved absorption and high bioavailability.
Clinical studies show that magnesium chelate forms, including magnesium glycinate and magnesium malate, offer enhanced absorption compared to non-chelated types. You absorb more magnesium from chelated magnesium because the chelate protects the mineral and helps it move through your gut. Magnesium chelate also causes fewer side effects, such as diarrhea, making it a better choice for many people.
| Magnesium Form | Absorption Rate | Bioavailability | Digestive Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium chelate | High | High | Gentle |
| Magnesium glycinate | High | High | Gentle |
| Magnesium oxide | Low | Low | May cause upset |
You can trust magnesium chelated blends to deliver improved absorption and high bioavailability. Choosing magnesium chelate means you get more of the mineral your body needs, with less risk of stomach discomfort. If you want to support your health, magnesium chelate is a smart option for improving magnesium absorption and overall wellness.
Health Benefits of Magnesium Chelate
Muscle and Nerve Support
You rely on your muscles and nerves every day for movement, coordination, and overall well-being. Magnesium chelate plays a key role in supporting these systems. When you choose chelated magnesium, you benefit from high bioavailability, which means your body absorbs more of the mineral. This helps maintain healthy nerve signaling and muscle contraction.
| Aspect | Evidence Summary | Supporting Details and Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|
| Neuroprotection | Chelated magnesium regulates calcium buffering and blocks NMDA receptors, preventing nerve injury and neurotoxicity. | Prevents secondary nerve injury, reduces cell death, and lowers neurotoxicity. Used clinically to lower cerebral palsy risk in preterm infants. |
| Anti-inflammatory Effects | Magnesium supplementation reduces inflammation in nerve tissue. | High magnesium diets improve neurobehavioral function and decrease inflammatory markers. Deficiency increases inflammation. |
| Promotion of Nerve Regeneration | Magnesium chelate promotes Schwann cell growth and axon regeneration. | Supports nerve growth and prevents cell death. Modulates proteins that control cell survival. |
| Biomaterial Applications | Mg2+ in biomaterials enhances nerve repair. | Mg2+-hybridized scaffolds support nerve regeneration in experimental models. |
Magnesium chelate supports muscle relaxation and helps your nerves recover from stress or injury. However, research shows that magnesium chelated blends do not significantly reduce muscle cramps in most adults. Studies found only a small difference between magnesium and placebo for cramp prevention. You may see some benefit if you have magnesium deficiency or are pregnant, but routine supplementation for cramps is not proven.
Tip: If you suspect magnesium deficiency, magnesium chelate may help restore nerve and muscle function.
Mood and Sleep
Your mood and sleep quality affect your daily health and energy production. Magnesium chelate benefits your brain by acting as a co-factor in hundreds of enzymes that regulate mood and stress reduction. Lower magnesium levels link to depression and anxiety. Some clinical trials show that magnesium supplementation, including magnesium glycinate, can improve depression scores and mood, especially when combined with other nutrients.
- Magnesium chelate helps regulate NMDA receptors and increases BDNF, supporting brain health.
- Magnesium deficiency often leads to low mood and poor sleep.
- Magnesium chelate blends may reduce symptoms of depression, but results vary by age, lifestyle, and health status.
- Magnesium chelate supports nervous system balance, which helps you manage stress and maintain sleep quality.
Magnesium chelate also improves sleep. Studies show that older adults taking magnesium chelate experience improved sleep quality, longer sleep duration, and better deep sleep stages. Magnesium glycinate and magnesium L-threonate are gentle on digestion and help you fall asleep faster. You may notice better mood, alertness, and daytime energy after using magnesium chelated blend supplements.
Note: Magnesium chelate is safe and well tolerated, making it a good choice for improved sleep quality.
Heart and Metabolic Health
Your heart health depends on minerals like magnesium. Magnesium chelate activates enzymes that regulate heart rhythm and blood pressure. High bioavailability ensures your body gets enough magnesium to support heart function. Magnesium chelate blends help lower blood pressure, especially in people with hypertension or magnesium deficiency.
- Magnesium chelate activates the Na+–K+ ATPase pump, which controls sodium and potassium in your cells. This helps regulate blood pressure and heart rhythm.
- Magnesium deficiency increases the risk of hypertension, arrhythmias, and inflammation.
- Clinical studies show that magnesium chelate supplementation can lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure by a few mm Hg.
- Magnesium chelate supports metabolic health by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing blood sugar levels.
- Magnesium glycinate and other chelated forms are gentle on your stomach and suitable for people with diabetes.
Magnesium chelate benefits include reduced inflammation, improved endothelial function, and better metabolic markers. You may see lower blood pressure, improved heart function, and better blood sugar control with regular use of magnesium chelated blend supplements.
Bone and Immune Support
You need strong bones and a healthy immune system for lifelong wellness. Magnesium chelate supports bone density by helping your body absorb calcium and activate vitamin D. Clinical studies show that magnesium supplementation increases bone mineral density in children, adolescents, and postmenopausal women.
| Study (Author, Year) | Population | Duration | Intervention | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stendig-Lindberg et al. (1993) | 54 postmenopausal osteoporotic women | 2 years | Magnesium tablets (250-750 mg/day) | 71% showed increased bone density; fracture prevention observed |
| Aydin et al. (2010) | 20 postmenopausal osteoporotic women | 30 days | 1830 mg magnesium citrate daily | Increased serum osteocalcin, decreased bone breakdown markers |
| Abraham and Grewal (1990) | 26 postmenopausal women | 6-12 months | Magnesium oxide + calcium citrate | 11% increase in bone mineral density |
| Carpenter et al. (2006) | 50 adolescents | 12 months | Magnesium supplementation | Increased hip bone mineral content |
| Wood et al. (2001) | 81 preadolescent girls | 1 year | Calcium, magnesium, vitamin D | Net gain in bone density |

Magnesium chelate also supports immune health. It acts as a cofactor in immune cell function and helps regulate inflammation. Magnesium deficiency leads to higher levels of inflammatory cytokines and weakens your immune response. Magnesium chelate blends help lower inflammation and support immune cell activation. You may notice fewer colds and better overall health when you maintain optimal magnesium levels.
Magnesium chelate benefits women with PMS and PCOS by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation. Some studies show magnesium chelate may help with menstrual pain and skin health, but results are inconsistent. You should talk to your healthcare provider before starting magnesium chelated blend supplements for these conditions.
Callout: Magnesium chelate offers high bioavailability, gentle digestion, and broad health benefits for bones, immune system, mood, sleep, and heart.
Chelated Magnesium vs. Other Magnesium Forms

Absorption and Effectiveness
You want your body to get the most from your magnesium supplement. Chelated magnesium stands out because it offers higher absorption and bioavailability than many other forms. When you take magnesium chelate, your body absorbs more of the mineral. This means you get better results for your health.
A comparison of common magnesium forms shows clear differences:
| Magnesium Form | Evidence Summary | Study Type | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium Oxide | Poor bioavailability compared to other forms; absorption influenced by formulation (e.g., effervescent tablets improve absorption). | Human clinical trials | Lower urinary Mg excretion; absorption improved with effervescent tablets due to better ionization. |
| Magnesium Citrate | Higher bioavailability than magnesium oxide, likely due to better solubility; difference sometimes marginal. | Human clinical trials | Slightly higher urinary Mg excretion than oxide; difference often physiologically irrelevant in some contexts. |
| Magnesium Amino Acid Chelates (e.g., aspartate, bisglycinate) | Generally higher bioavailability than magnesium oxide; comparable or sometimes superior to citrate. | Human clinical and in vitro studies | Higher absorption rates; chelated forms show superior solubility and bioavailability. |
| Magnesium Gluconate | Highest absorption in animal models (rats). | Animal studies | Most efficient absorption compared to other salts in rat intestine studies. |
You see that chelated magnesium, such as magnesium chelate and magnesium glycinate, often outperforms magnesium oxide and matches or exceeds magnesium citrate. An in vitro study found that magnesium bisglycinate, a chelated form, had much higher absorption than both magnesium oxide and citrate. This means your health can benefit more from chelated magnesium blends.
Digestive Tolerance
You may worry about stomach upset when taking magnesium. Chelated magnesium blends are gentler on digestion than non-chelated forms. Magnesium chelate does not draw water into your intestines, so you are less likely to experience diarrhea or cramping.

Magnesium glycinate, magnesium lactate, and magnesium malate are chelated forms known for their digestive comfort. You can take these even if you have a sensitive stomach. Clinical studies and patient surveys show that chelated magnesium causes fewer side effects than magnesium oxide or citrate. Most people report little to no digestive discomfort with magnesium chelate.
Tip: If you need daily magnesium for health, chelated magnesium blends offer high bioavailability and gentle digestion. Many people choose these blends for better absorption and fewer side effects.
You may also notice that magnesium chelated blends support multiple areas of health, including sleep, energy, and muscle recovery. This makes them a popular choice for people who want a full-spectrum approach to wellness.
How to Use Chelated Magnesium for Wellness
Choosing the Right Blend
You want to select an effective supplement that matches your health goals. When you shop for magnesium supplements, check the label for the amount of elemental magnesium, not just the compound name. Look for chelated magnesium forms like magnesium glycinate or magnesium citrate, which offer better absorption and gentle digestion. If you need support for sleep or relaxation, magnesium glycinate works well. For digestive comfort, magnesium citrate or lactate may help. Magnesium malate and orotate support energy and heart health.
| Type of Chelated Magnesium | Chelating Molecule | Bioavailability | Key Benefits / Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium Glycinate | Glycine | High | Relaxation, mental calm |
| Magnesium Citrate | Citric acid | Good | Digestion, mild laxative |
| Magnesium Orotate | Orotic acid | Good | Heart health |
| Magnesium Malate | Malic acid | Good | Energy support |
You can choose capsules, gummies, drinks, or sprays based on your preference. Always check for third-party testing to ensure quality. Consider the flavor and ease of use if you plan to take magnesium daily. Compare prices by looking at the cost per recommended dose.
Tip: Take magnesium with meals and avoid combining it with other mineral supplements at the same time for best absorption.

Dosage and Safety
You should follow recommended guidelines for magnesium supplementation. Most adults need between 310 and 420 mg of elemental magnesium each day. Supplements usually provide 200 to 400 mg per dose. The safe upper limit for supplemental magnesium is 350 mg daily. If you have a deficiency, your doctor may suggest a higher dose, but only under supervision.
| Group | Europe (EFSA AI) | USA (NIH RDA) |
|---|---|---|
| Adult Men | 350 mg/day | 310-420 mg/day |
| Adult Women | 300 mg/day | 310-320 mg/day |
| Pregnant Women | 300 mg/day | 350-360 mg/day |
| Lactating Women | 300 mg/day | 310-320 mg/day |
You should avoid magnesium supplements if you have kidney disease unless your doctor approves. People with kidney problems risk high magnesium levels, which can cause symptoms like nausea, muscle weakness, and slow heartbeat. Monitor your magnesium levels with regular blood tests if you have health concerns.
Note: The most common side effects of chelated magnesium include mild stomach upset, nausea, or diarrhea. These forms are less likely to cause problems than non-chelated types.
Start with the lowest effective dose and increase slowly. Take magnesium with food to reduce stomach discomfort. If you notice side effects such as diarrhea or muscle weakness, talk to your healthcare provider. Store your supplement in a cool, dry place to keep it fresh.
You can support your health by choosing magnesium chelated blends. These supplements help your muscles, heart, bones, and mood. Experts recommend picking the right form for your needs and checking for third-party testing. Magnesium chelate works in over 300 body processes and helps your immune system stay strong.
| Area | How Magnesium Chelate Helps |
|---|---|
| Muscle | Improves function and recovery |
| Heart | Supports rhythm and blood pressure |
| Bone | Increases density and strength |
| Mood & Sleep | Boosts emotional well-being and rest |
| Metabolism | Aids energy and immune response |
Start adding magnesium chelated blends to your daily routine. You can take charge of your wellness and feel your best every day.
FAQ
What is the best time to take magnesium chelated blends?
You can take magnesium chelated blends with meals. Many people prefer taking them in the evening to support sleep. Taking magnesium with food helps your body absorb it better and reduces the chance of stomach upset.
Can you take magnesium chelated blends every day?
You can use magnesium chelated blends daily. Most people need 310–420 mg of magnesium each day. Always check the label for dosage and talk to your doctor if you have health concerns.
Are magnesium chelated blends safe for children?
Children can use magnesium chelated blends if a doctor recommends them. You should follow age-appropriate dosages. Magnesium supports growth, bones, and nerves. Never give supplements to children without medical advice.
Do magnesium chelated blends interact with medications?
Some medicines, like antibiotics or diuretics, may interact with magnesium. You should ask your doctor or pharmacist before starting magnesium chelated blends if you take prescription drugs.
What are common side effects of magnesium chelated blends?
Most people tolerate magnesium chelated blends well. You may notice mild stomach upset or loose stools. These side effects usually go away if you lower your dose or take magnesium with food.

Poseidon
Master of Nutritional Epidemiology, University of Copenhagen, Herbal Functional Nutrition Researcher
Focus: The scientific application of natural active ingredients such as Tongo Ali, Horny Goat Weed, and Maca to sexual health and metabolic regulation.
Core Focus:
Men: Use a combination of Tongo Ali (an energizing factor) + Maca (an energy reserve) to improve low energy and fluctuating libido.
Women: Use a combination of Horny Goat Weed (a gentle regulator) + Maca (a nutritional synergist) to alleviate low libido and hormonal imbalances.
Stressed/Middle-Aged Adults: This triple-ingredient synergy supports metabolism, physical strength, and intimacy.
Product Concept:
Based on traditional applications and modern research (e.g., Tongo Ali promotes testosterone-enhancing enzyme activity, and icariin provides gentle regulation), we preserve core active ingredients and eschew conceptual packaging—using natural ingredients to address specific needs.
Simply put: I'm a nutritionist who understands "herbal actives." I use scientifically proven ingredients like Tongo Ali, Epimedium, and Maca to help you make "sexual health" and "nutritional support" a daily routine.